SWS2 Penetration Testing 1
Penetration Testing
Goals
- name six different testing methods and discuss which method is best when given the task of doing a security test
- be able to explain penetration testing
- name at least two standards providing guidance on how to do penetration testing
- explain the role and important parameters (scope, rules of engagement, test method) of the pre-engagement phase
Reasons
Why do we want to test? What’s our goal?
Find and fix vulnerabilities? Or test the incident response processes and capabilities?
What do we want to test?
- single service
- entire organisation
Who should do the testing?
- Members of our Staff
- 3rd party
- crowd
automated test or human?
live system or source code
Security Testing Methods
- Vulnerability Scanning
- Classical Penetration Testing
- Red Teaming / Ethical Hacking
- Purple Teaming
- Breach & Attack Simulation
- Bug Bounty Progam
Vulnerability Scanning
| Purpose | Identify well-known vulnerabilities |
| Attacker Goal | - |
| Assets in Scope | Source code, applications, systems, entire infrastructures |
| Result | Potential vulnerabilities and generic risk rating |
| Method | Fully automated (software / appliance / SaaS) * e.g., OpenVAS (infrastructure), LGTM.com (source code) |
| Requirement | Mature vulnerability management process * resources/skills to verify, priotize and fix them |
| Frequency | Continous * Vulnerability signatures and assets are not static |
Classical Penetration Testing
| Purpose | Find as many vulnerabilities as possible and get fixing advice (Compliance (GDPR,HIPAA,PCI DSS,..) |
| Attacker Goal | find many vulnerabilities efficiently manly easy find vuln. |
| Assets in Scope | One / a few |
| Result | verified vulnerabilities and their risk rating plus advice how to fix them |
| Method | (semi)-automated tools/scanners and standardized testing procedures (for web-apps. e.g. OWASP testing guide |
| Requirement | Mature vulnerability management processes, testing env. |
| Frequency | 1-4 times a year / once per version |
Red Team Testing
| Purpose | Test the organizations detection and respons capabilites |
| Attacker Goal | Find a way to achieve a stated goal and don’t get caught trying * e.g. steal customer data, become Domain Admin, install spyware on a designated asset |
| Assets in scope | Many / all (physical, human, cyber) |
| Result | Goal achieved (yes/no) and how it was achieved |
| Method | Goald and scope dependent, often social engineering |
| Requirement | Mature security program - i.e., vulnerability mgmt, security testing & monitoring, and incident handling in place |
| Frequency | periodically |
Purple Team Testing
| Purpose | improve security posture * focuse on detective/preventive contorls *identify malicious actors in environment |
| Attacker Goal | help the blue team to catch them / learn from them |
| Assets in scope | predetermined systems/employees |
| Result | improvements to security controls (e.g., new detection rules) and plan to resolve issues that could not be addressed during the exercise |
| Method | Simulate (relevant) attacke patterns and scenarios |
| Requirement | interfaces and collaboration between incident response, security tooling, network engineers and vulnerability management work well |
| Frequency | Periodically (e.g. once per quarter |
the BAD build, attack, defend pyramid
Breach & Attack Simulation
| Purpose | Improve security posture: *focus on detective controls -use a set of “prominent” attack vectors (e.g MITRE ATT&CK) -Usually, multi-step attacks along the cyber kill chain |
| Attacker Goal | - |
| Assets in scope | Any* (determined by the selected attack types/scripts |
| Result | Report on resilience against the scripted cyber attacks |
| Method | Automated testing platform (e.g. SaaS) implementing scripted multi-stage attacks (e.g, implementing the steps in the cyber kill chain |
| Requirement | same as purple team testing, big-bugdget blue-team |
| Frequency | continous |
Bug Bounty Programm
| Purpose | Find vulnerabilities and pay only if vulnerabilities are found - Public > anyone can perticipate - Private > selection process / by invitation only |
| Attacker Goal | Earn money or prestige |
| Assets in scope | Often a singel app/service/system |
| Result | Vulnerability Report |
| Method | According to the program - specifies what is allowed |
| Requirement | appropriate legal framework, willingness to go public accept not knowing the testers |
| Frequency | continous |
When to apply which method
| Vulnerability Scanning | Penetration Test | Red Teaming | Purple Teaming | Bug Bounty | Breach & Attack Simulation | |
| finding known vuln | x | x | (x) | |||
| find vuln. in self dev. apps | (x)1 | x | x | |||
| ipmrove prod sec. | (x)1 | (x)2 | x | |||
| ipmprove defensive measure | x | x | ||||
| Test defenses, incident response | x | (x) | x | |||
| Educate/train blue team | (x) | x | (x) | |||
| compliance | x | (x) |
Penetration testing Phases
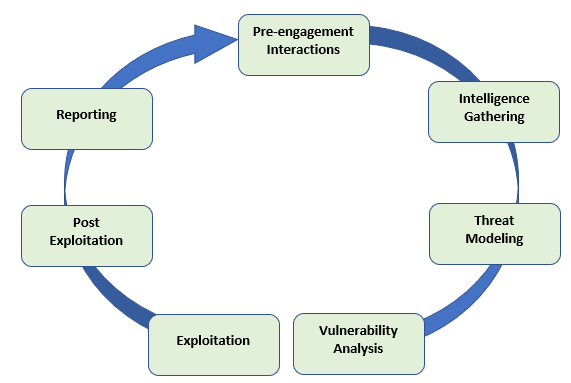
-
Specialized Scanners. Specialized scanners. Can detect vulnerabilities that can be found with “simple” testing patterns (e.g., web application scanners looking for SQL injection or XSS vulnerabilities) under the condition that the vulnerable item/action in the application/system can be found/triggered (e.g., web form supplying the data) by the scanner. ↩︎ ↩︎
-
Pen testing can help here, but activities earlier in the product development cycle are far more effective and should be prioritized (e.g., threat modelling, security architecture review, code review and static code analysis) ↩︎